L-Methionine is a sulfur-containing essential amino acid that plays a vital role in tissue growth and repair as well as in the growth of new blood vessels. It is part of many biochemical reactions, including the production of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM or SAMe). SAM is partly involved in the synthesis of creatine, epinephrine, and melatonin along with several other substances.
It also promotes healthy skin, hair, and nails and is involved in the body’s natural detoxification process by protecting cells from pollutants and slowing down cell aging. Moreover, it is also crucial for the absorption and bioavailability of selenium and zinc.
How It Works
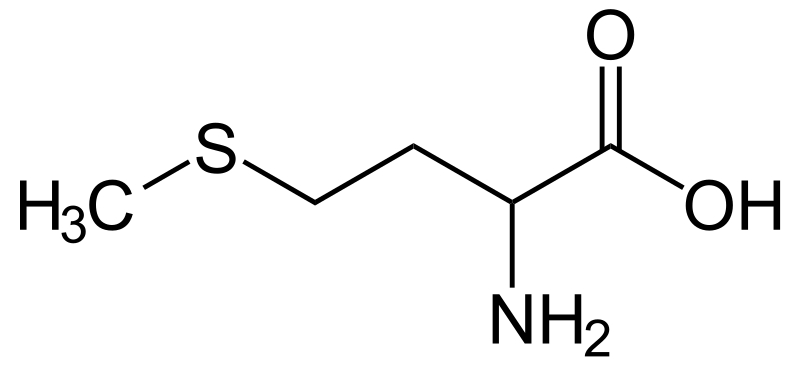
Methionine plays a crucial role in the metabolism and health of humans. It is the substrate for other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine as well as for compounds like SAM-e and the antioxidant glutathione.
It also contains sulfur and can produce other sulfur-containing molecules that the body uses to make proteins in the body. It also plays an important part in the growth of new blood vessels.
L-Methionine Benefits
- Methionine helps improve athletic performance by building bone strength. It adds bone volume, mineralization, and mineral content which improves your ability to perform high-intensity physical activities.
- It aids in weight loss through its role in creating creatine in the body. It helps improve athletic performance as well as the muscle to fat ratio in the body.
- When combined with other B vitamins, methionine may help reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
- Studies have also shown that patients treated with l-methionine for two weeks to six months can lower tremors in Parkinson’s patients. It also helps prevent the effects of dopamine damage and dopamine loss.
Dosage Recommendations for L-Methionine

Generally, the body can produce its own methionine. However, supplementation may be necessary for people experiencing certain illnesses. This includes Parkinson’s disease, drug withdrawal, schizophrenia, radiation, copper poisoning, asthma, allergies alcoholism, liver damage, and depression.
According to the World Health Organization, the daily recommended dosage for l-methionine depends on a person’s age. For pre-school children ages 2 to 5, the recommended dose is 27 mg/kg of body weight per day. School-aged children ages 10 to 12 should be taking 22 mg/kg of body weight per day. Meanwhile, adults over 18 years of age need 12 mg/kg of body weight per day.
You can source it from your diet. Some food with the highest concentrations of L-methionine includes egg whites, chicken halibut, tuna, cod, turkey, seaweed, spirulina, sesame seeds, and oats. There are also dietary supplements available in the market.
Safety Considerations for L-Methionine
Overconsumption of methionine can lead to minor side effects. This includes dizziness, sleepiness, and changes in blood pressure. While the side effects are considered minor, extremely high doses could be dangerous.